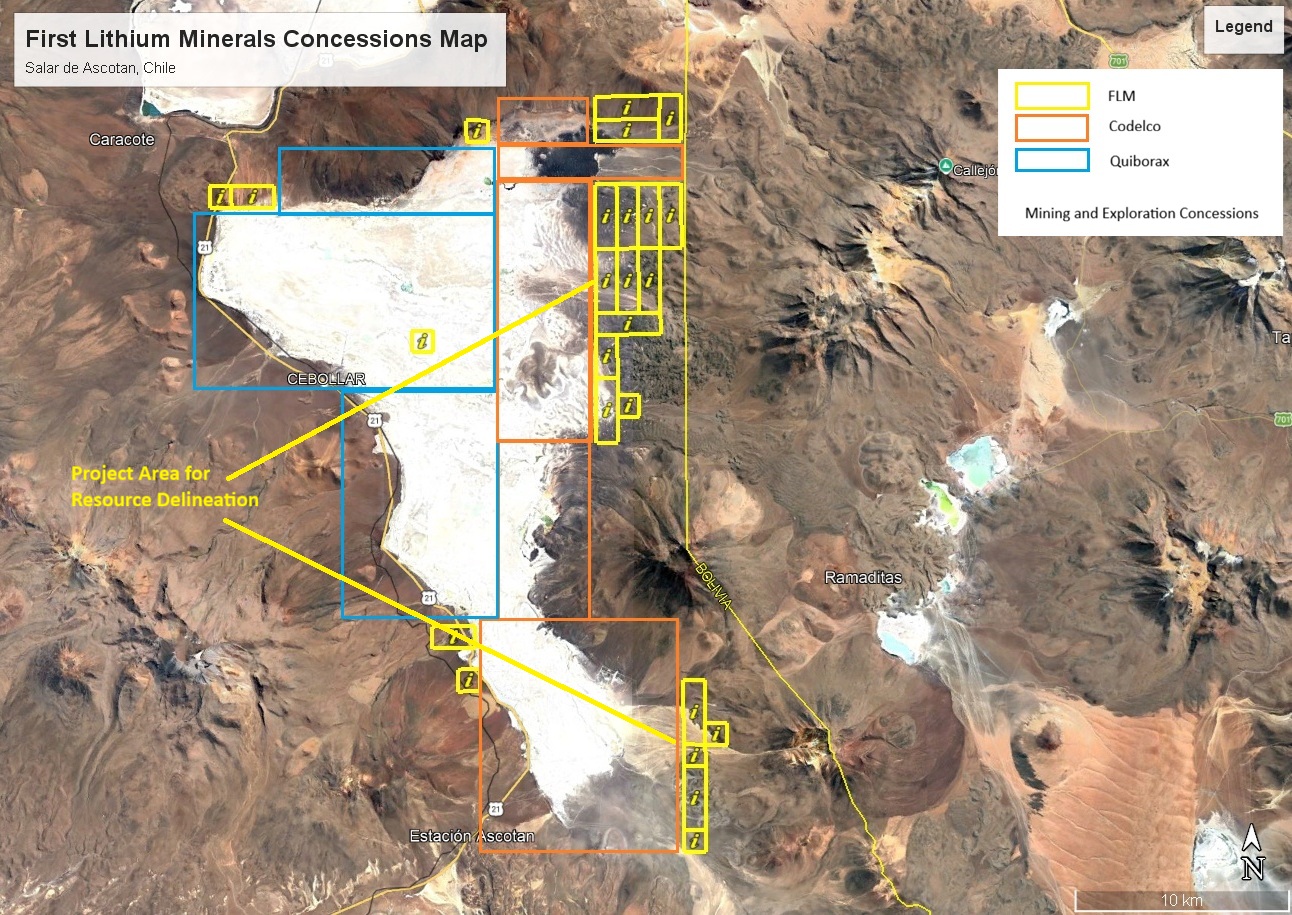
OCA SALAR DE ASCOTAN PROJECT
Approx. 1,800 ha of mineral exploration concessions located in the salar Ascotan in the Antofagasta Region of northern Chile within the cordilleran sector bordering Bolivia.
INFRASTRUCTURE
- The OCA Salar de Ascotan Project is accessed from the town of Calama, Chile via Highway 21, 150 km
- The town of Ollague is at an elevation of 3,700 meters above sea level and is the closest to the OCA Salar de Ascotan Project
- The railway (The Ferrocarril de Antofagasta a Bolivia, “FCAB”) that passes through Ollague forms he major transportation corridor between the port city of Antofagasta, Chile and the capital city of Bolivia, La Paz
- Historically, primary rail transport has been lead-zinc concentrates, nitrates, and copper
- Cerro Pabellon Geothermal Power Plant located approximately 70km south of the project
- Multiple operating copper mines in the area
TOPOGRAPHY
- The salar basin is bordered on the north by the Salar de Carcote basin, on the east by volcanic chains bordering Bolivia
- To the south, the basin is bordered by the San Pedro de Inacaliri River basin, while to the west the basin is cut-off by a volcanic chain summits from the drainage of the Upper Loa River
EXPLORATION TARGET
- 1,800 ha of exploration concessions that form the project focus area (eastern sector) for on-going exploration and potential resource delineation target
- The eastern flank is at the continental divide formed by the Andes: the Paruma de Portezuelo mountain (5,582 meters above sea level), the Ollagüe volcano (5,868 meters asl), the Ascotán mountain (5,187 meters asl) and the Toconce mountain (5,411 meters asl)
- Climate is arid, with average annual precipitation < 100 mm
- Little to no biodiversity in the targeted exploration sector
- Project area altitude 3,716 msnm
- Desert environment
- Soft and hard saline crusts and clay playas
- Existing commercial production of borates on the western flank of the salar
MINERALIZATION
Mineralization in the OCA Salar de Ascotan Project is primarily represented by three different fractions:
- Liquid, represented mainly by chloride and sulfate brines
- Dendritic material, consisting of sand, silt and clay intercalated in the salar sediments
- Various precipitated salt compounds resulting from salts reaching respective solubility and concentration limits
HYDROGEOLOGY
- Salar de Ascotan corresponds to a classic continental ‘saline deposit’ type or the Salar
- Lithium (Li), potash (K), boron (B), sodium (Na) and magnesium (Mg), among others, are leached and transported from rocks in the catchment, and then accumulated and concentrated by evaporation in the Salars
- Geology and hydrogeology extensively studied and investigated by SQM, Codelco and Chilean Geological Surveying
- Salar de Ascotan: 1,757 km2 (basin area), 243 km2 (surface area)
- The Salar is a terminal lake with sediments intermixed with salt compounds, undersurface brine, and a surface crust composed primarily of gypsum and halite
- Groundwater of the Salar show characteristics of a typical brine observable a few meters below the surface